Cord blood as a source of stem cells
In 1983, it was discovered that umbilical cord blood can serve as an amazing source of stem cells. However, it wasn’t until 1988 that the first successful cord blood transplant was carried out. Since then, cord blood has been used to treat a wide range of diseases, including blood disorders, autoimmune/metabolic disorders, and several types of cancers.
Stem cells can be extracted from three different sources – cord blood, bone marrow, and peripheral blood. Cord blood is much more significant than the other sources; it is safe and painless to harvest, can be set aside for years after extraction, and has been able to treat more than 80 types of diseases.
What is Cord Blood?
Cord blood is short for umbilical cord blood, which is the blood present in the umbilical cord and placenta right after childbirth. The umbilical cord blood contains hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), an undeveloped cell that can morph into any type of blood cell (including white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets). As a result, HSCs are used to treat diseases that affect the functioning of the circulatory and immune systems.
How Is It Collected?
Harvesting umbilical cord blood is not as tedious and risky as it sounds. In fact, there are absolutely no health risks related to cord blood collection. There is absolutely no harm to the newborn baby during the collection process. Once the baby completely leaves the birth canal and the umbilical cord is cut off, there is a decent amount of ‘leftover’ blood in the cord and around the placenta.
You have two options here: throw the cord away or save it for future use. There are numerous cord blood banks in the U.S. and around the world that can bank and preserve your child’s cord blood. You can save it for your child to use in the future, for a family member who may need it, or donate it to others who need it.
Keep in mind, not all hospitals offer this service and those that do may even require a separate fee to obtain the cord blood. If you have any questions or would like to bank your child’s cord blood, to donate or not, let your doctor know about 6 weeks before your due date. If your hospital does not offer cord blood banking, you may have to contact the cord blood bank to organize the harvest.

What Conditions Does It Treat?


- Sickle cell disease, Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome, Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID), Neutropenias, Phagocyte Disorders
- Non Malignant Blood Disorders: Anaemias, Hereditary Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes, Inherited Red Cell Abnormalities, Inherited Platelet Abnormalities
- Metabolic Disorders: Leukodystrophy Disorders, Lysosomal Storage Diseases, Mucopolysaccharidosis Storage Diseases
- Solid Tumors: Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, Neuroblastoma, Burkitt’s Lymphoma, Retinoblastoma, Medulloblastoma
- Blood Cancers: Leukemia, Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
The discovery of Cord blood has been one of the most significant breakthroughs in history. The success can definitely be measured by the millions of people who suffer from various diseases and who have been helped by it.
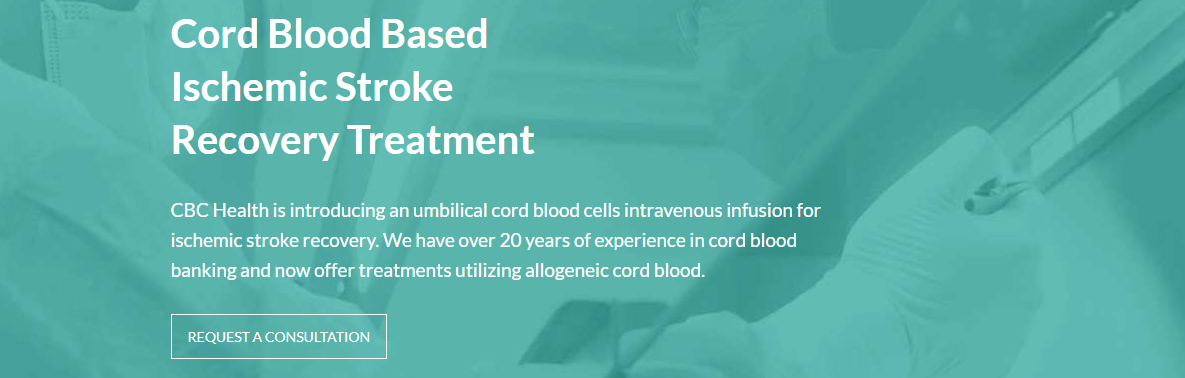
Benefit from our experience in cord blood banking & stem cell treatment
CBC Health has over 20 years of experience in cord blood banking. We offer stem cell treatments for those who have suffered an ischemic stroke, utilizing cells derived from allogeneic cord blood.
Learn about our revolutionary stroke treatment and how cord blood can save lives! For more information, contact us at +1 855 426 4623.